Induction Brazing
Induction brazing is the process of joining two or more metals using induction heating. Induction heating utilizes the electromagnetic field to provide heat without contact or flame. Induction brazing is more localized, repeatable, and easier to automate compared to traditional torch brazing.
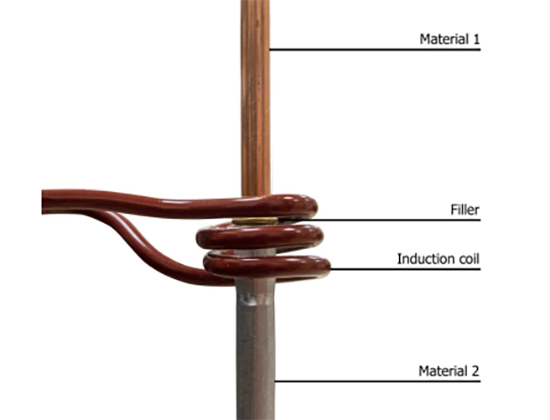
Induction brazing has been around for a long time but is only now coming into wider use due to advancements in induction heating power supplies.
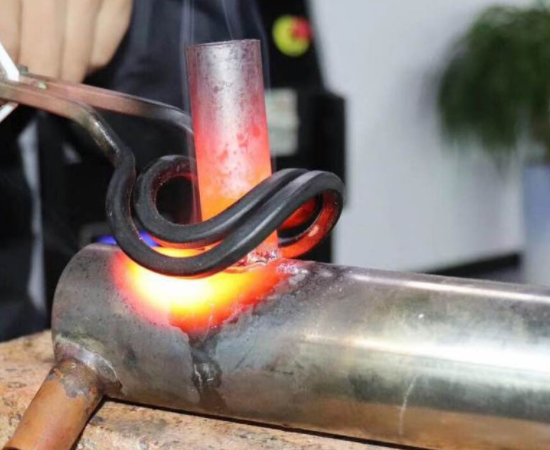


The principle of induction brazing is similar to the transformer principle, where the inductor is the primary winding and the part to be heated acts as a single turn secondary winding.
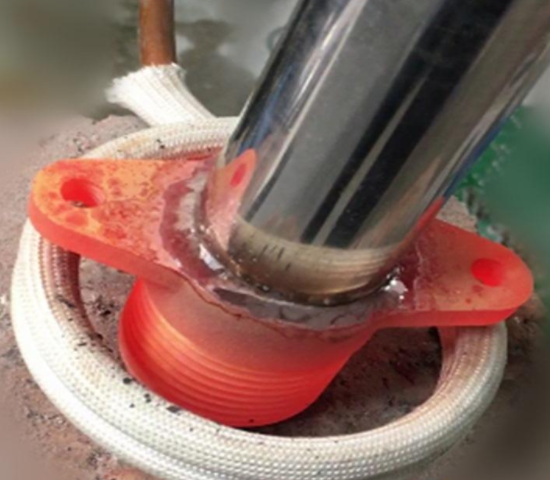
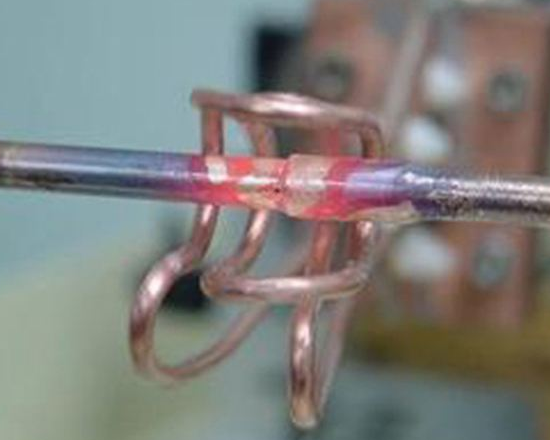


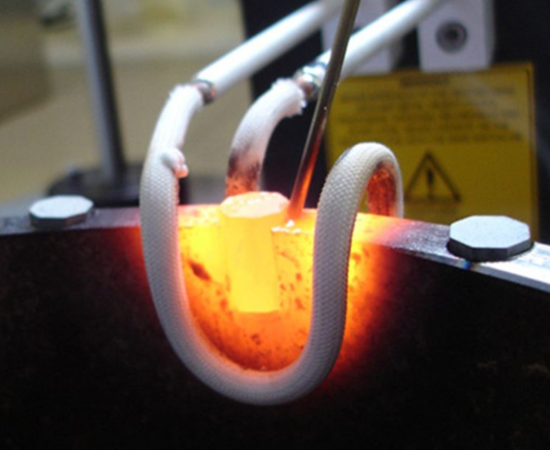

The main advantage of induction brazing is its precisely localized heat. The induction heating coil can be placed directly on the joint, providing a more consistent amount of heat than a torch. Another advantage is that induction brazing is more repeatable than traditional brazing. The induction brazing process has a predictable heat profile (essentially, the amount of heat provided over time), which is more consistent than traditional brazing and can be automated. It does not depend on operator’s skills as much as the torch brazing.
- Pre: Induction Hardening
- Next: Induction Melting
 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français